On this page (click to jump):
Claire Oudea Gan Li, CS 22/122: 3D Digital Modeling, 2025
ACADEMICS
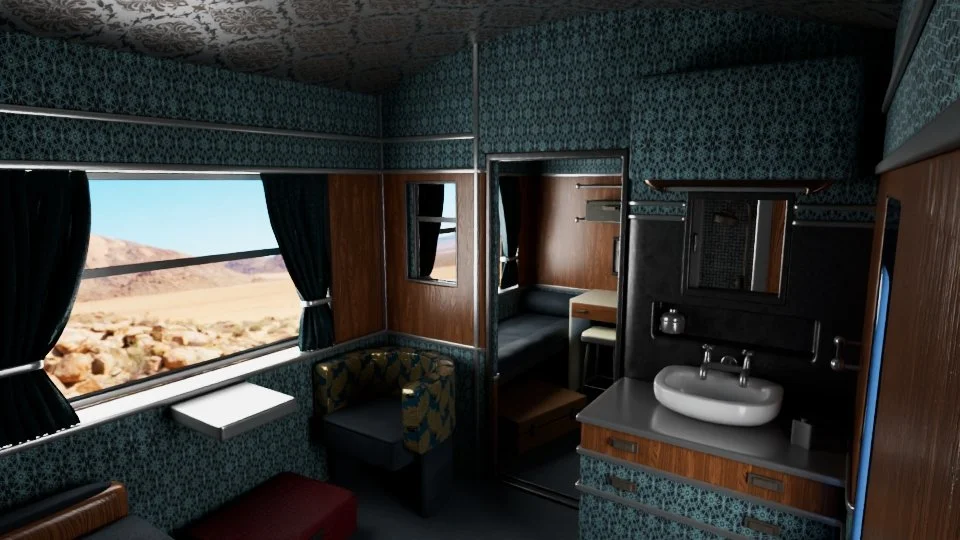
The intersection of art and technology is a quickly growing area with tremendous room for innovation and creativity. The Digital Arts MS program at Dartmouth covers a wide range of topics within computer science along with many areas of arts, including HCI, computer graphics, computer modeling and animation, AR/VR/MR, computational photography, UI/UX design, data visualization, digital music, computational fabrication and 3D printing, interactive installations, and machine learning for art.
CURRICULUM
The MSDA curriculum is divided into three areas: Technical Courses (general graduate level computer science courses), Digital Art Courses, and Research/Thesis Courses. At the end of the program, all students will write a thesis based on their research and then present and defend their work.
Courses required for the degree will depend on the background of each student. All students must take 18 credits of which up to 12 will be coursework and up to 9 will be research credits. For a formal description of the degree and course requirements, please consult the ORC.
REQUIREMENTS
Prerequisites: two courses out of COSC 30 (Discrete Math), COSC 31 (Algorithms), COSC 50 (Software Design and Implementation), COSC 70 (Foundations of Applied Computer Science).
Technical Courses: at least five Computer Science courses numbered in the ranges 131—189 or 231—289. At least one must be an advanced topics graduate course in Computer Science (listed as COSC 149/249, COSC 169/269, and COSC 189/289). These include courses in theory, computer vision, computer graphics, human-computer interaction, machine learning & AI, robotics, and more. See the available courses in the ORC and the upcoming class schedule.
Digital Arts Courses: at least two courses in digital arts (see list below) or a related arts field.
Research: at least six course equivalents of research from COSC 294, COSC 297, COSC 298, or COSC 299.
Thesis: see our outcomes & rubrics for a successful thesis and defense.
Thesis research projects might include:
Creating a work of art using computational methods
Developing new software that makes arts easier to create or more effective to use
Creating new interactive digital arts experiences that bring new understanding to the human experience
Building new tools/techniques for animation, modeling, computational photography, 3D fabrication, or games
Utilizing machine learning algorithms for art creation
Computationally created fashion and accessories
UNDERGRADUATE MINOR
No previous experience in computer science or digital arts is required. Our goals are to (1) teach students the principles, aesthetics and practice of digital art, modeling and animation through hands-on exercises and assignments, (2) provide an understanding of technical concepts in order to allow students optimal control over the tools being used to create digital art, (3) offer an opportunity for students from different disciplines to work together, and (4) create a minor that is comprehensive and deep, through focused assignments and a demand for proficiency and high production values.
For a formal description of the minor requirements, please consult the ORC.
REQUIREMENTS
One prerequisite course: COSC 1, COSC 2, or ENGS 20.
Any three courses between CSDA 20 and 29.
Two other courses, at most one of which is COSC, from the list of approved additional courses for the Digital Arts minor in the ORC. These include courses that teach the principles and practice of art, design, filmmaking, animation, music, games, and theater.
COURSES
Note! Starting in Fall 2025, the prefix for all Digital Arts courses changed from COSC to CSDA.
-
This projects-based course will familiarize students with the fundamentals of digital design, including layout, text, color theory, and UI design. Foundational concepts and the universal principles of design will be explored through extensive analyses and a series of design projects. No previous art or technical experience is required. Work is evaluated on a set of technical and aesthetic criteria and class participation.
-
This projects-based lab course teaches the principles and practices of 3D modeling. Lectures focus on principles of modeling, materials, shading, and lighting. Students create a fully rigged character model while learning their way around a state-of-the-art 3D animation program. Assignments are given weekly. Students are graded on the successful completion of the projects, along with a midterm examination. Work will be evaluated on a set of technical and aesthetic criteria.
-
This hands-on projects-based course exposes students to the aesthetic, technical, and societal issues surrounding the emerging frontiers of digitally mediated realities. Students learn the fundamentals of augmented and virtual reality design and are introduced to interactive development for VR/AR. CSDA 23/123 and COSC 63.01 have class together and work together on teams. Designers in this course create assets and design the UI/UX while developers build interactive digital tools, games, and visualizations. This course is not open to students who have received credit for COSC 29.22 or COSC 89.22. Additional assignments will be given to graduate students.
-
This hands-on course focuses on state-of-the-art computer animation, presenting techniques for traditional animation and how they apply to 3D computer animation, motion capture, and dynamic simulations. Facial and full-body animation are covered through projects, readings, and presentations, including physical simulation, procedural methods, image-based rendering, and machine-learning techniques. Students will create short animations. This course focuses on methods, ideas, and practical applications, rather than on mathematics.
-
CSDA 125.01 is a hands-on projects-based course that teaches the concepts, principles, and practice of User Interface (UI) and User Experience (UX) Design. It is designed for students with an interest in any form of design, although we focus on the UI/UX of digital tools (e.g. mobile, web, tablets). No previous experience or coding skills needed. Grading is based on weekly assignments, reflections, readings, and in-class exercises that build on each other and are intended to teach the foundational skills and thinking of UI/UX design. This team-based course requires a significant amount of time outside class. Students are encouraged (but not required) to take ENGS 12 prior to taking this course.
-
This Independent Study course offers students who have taken CSDA 125.01 a chance to put what they learned in the classroom into practice. Students might work as a designer in the DALI Lab or on another project. In addition to completing a project as a designer, students design and build an online portfolio.
-
This is the culminating course for the Digital Arts Minor. Students complete projects in digital arts, including: computer animations; games, VR/AR applications, interactive digital installations and media. Students work in small teams to complete work of a high production quality or work that incorporates innovations in technology. Grades are based on aesthetic and technical criteria along with teamwork and adherence to weekly milestones.
-
Artists, designers, creators, and makers increasingly use digital fabrication methods in both two and three dimensions as a means of designing, rapid prototyping and manufacturing. This class uses digital fabrication tools in a studio setting. Students learn digital fabrication through a series of 2D and 3D design projects and through critical discussions of the aesthetic, sociological and practical implications of integrating digital tools and materiality into the design and build process.
Students will have hands-on training in the process of creating and converting computer generated drawings and models into physical objects through the use of 2D and 3D scanners, laser-cutters, wire benders, cnc routers and 3D printers. No previous experience needed.
-
As computation becomes ubiquitous, we find interactive digital devices scattered around our homes, as integral parts of our living environments, including smart appliances, interactive architectural elements, toys, and interactive artworks. Digital Tangible User Interfaces (TUIs) are an approach to Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) where computation is embedded into objects we can interact with. One challenge of the TUIs is how to create a seamless interface between users and digital information so that the user can naturally interact with the daily product and their living environment. This course will focus on the theory, process, and practice of building intelligent objects and spaces. Students will be required to design and implement tangible user interface projects by using physical computing tools (Arduino) and computer languages such as Processing.